Now Reading: Is a US recession coming? 5 key questions answered
-
01
Is a US recession coming? 5 key questions answered

Is a US recession coming? 5 key questions answered
The US financial system could also be heading into tough climate — and when America slows down, the world feels the tremors. With Trump tariffs placing international commerce below stress and India carefully tied to each the US and China, a doable recession within the US can, on the very least, decelerate development charge in India too.Here’s what economists and traders are saying:
5 key questions answered
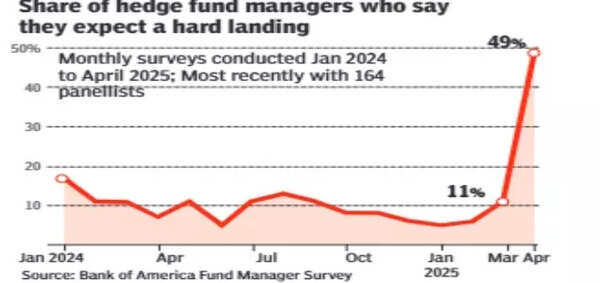
1. How shut is US to a recession?
Five companies and specialists have following to say:
| Agency | Key Reasons |
|---|---|
| Tariffs, fading fiscal impulse, and tight credit score requirements | |
2. US recessions since 2000
| Recession | Peak | Trough | Duration (months) | Real GDP peak-to-trough | Peak Unemployment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dot-com / Sept. 11 | Mar 2001 | Nov 2001 | 8 | –0.3% | 5.7% |
| Great Recession | Dec 2007 | Jun 2009 | 18 | –4.0% | 10.0% |
| Covid-19 Recession | Feb 2020 | Apr 2020 | 2 (shortest on report) | –19.2% (q/q annualized Q2) | 14.7% |

3. Can US recession set off international recessions?
US recessions can go international after they coincide with a systemic monetary shock (2008) or an exogenous occasion (pandemic). Otherwise, spill-overs are milder. IMF has dominated out a international recession.
- 2001 US recession didn’t trigger a international one. World GDP grew 2.5%, however commerce development collapsed.
- 2007–09 was a US & international recession — first post-war international contraction (~1.3% world GDP ’09)
- 2020 Covid lockdown pushed world GDP down by ~3%, deepest since 1945
4. China & India recessions since 2000
Periods of outright GDP contraction (previous 25 years)
China
- Q1 2020 (–6.8% y/y) – first contraction since 1976
Notes: Annual development nonetheless +2.2% for 2020; 2022 development simply 3% (worst exterior 2020)
India
- FY 2020-21 (–7.3%, with –24% in April–June 2020); RBI categorised H1 FY21 as a “technical recession”
Notes: Previous near-recessions
- 1991 balance-of-payments disaster (actual GDP +1%)
- 2008-09 slowdown (development fell to three.1%, however stayed constructive)
5. Why a recession in India is completely different from one within the US
| Dimension | United States | India |
|---|---|---|
| General nature of major shock | Financial cycle & client credit score (housing, bank cards); stock cycle | |
| Stabilising elements | Large: Unemployment insurance coverage, progressive taxes mitigate hit | Small; Informal employment > 45% limits social-security attain |
| Monetary-policy pass-through | Fast: Deep bond market, mortgage refinance | Slower; Bank-led system, excessive share of small corporations exterior formal credit score |
| Job & Wages | Unemployment rises sharply however advantages cushion earnings | |
| Global spillover |






