Now Reading: Two-headed hyphalosaurus: Fossil discovery reveals rare dinosaur anomaly |
-
01
Two-headed hyphalosaurus: Fossil discovery reveals rare dinosaur anomaly |

Two-headed hyphalosaurus: Fossil discovery reveals rare dinosaur anomaly |
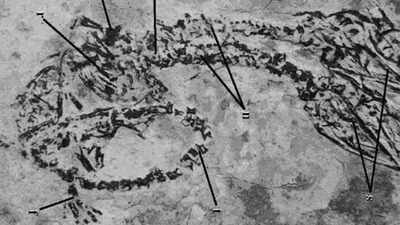
A outstanding fossil discovery courting again greater than 120 million years has revealed the existence of a two-headed Hyphalosaurus, a small, long-necked aquatic reptile that lived in the course of the Early Cretaceous interval. Unearthed within the Yixian Formation of northeastern China, this distinctive specimen exhibits clear indicators of axial bifurcation, a rare developmental anomaly by which an embryo begins to separate into twins however fails to finish the method, leading to a single organism with two heads.Although related malformations have been noticed in modern-day reptiles reminiscent of snakes, lizards, and turtles, this fossil is the oldest recognized instance of such a situation within the vertebrate fossil report. The discovery, revealed in a 2007 examine by Buffetaut and colleagues in Biology Letters, gives vital perception into the incidence of congenital defects in historical species. It additionally offers a captivating glimpse into the organic and evolutionary challenges confronted by early reptiles, including a rare developmental perspective to paleontology and evolutionary biology.
Fossil discovery explains axial bifurcation in two-headed hyphalosaurus
Axial bifurcation is a rare developmental anomaly that happens throughout early embryonic progress, the place the vertebral column begins to separate longitudinally, leading to two parallel cervical (neck) sequence and the formation of two distinct skulls and necks. This incomplete twinning course of results in the event of conjoined heads, a situation that’s extraordinarily unusual in reptiles and different vertebrates. In fashionable species reminiscent of snakes and turtles, axial bifurcation is sometimes noticed however normally ends in non-viable or short-lived offspring resulting from problems in mobility, feeding, or organ operate.The two-headed Hyphalosaurus fossil found within the Yixian Formation offers the earliest recognized proof of this phenomenon within the fossil report. Measuring simply 70 millimeters in size, the specimen is believed to be both a late-stage embryo or a new child that didn’t survive past hatching. Despite its temporary lifespan, the fossil’s distinctive preservation gives scientists a rare window into congenital malformations in historical reptiles. It not solely demonstrates that such developmental errors occurred way back to the Early Cretaceous but in addition opens new avenues for understanding the evolutionary and genetic components influencing vertebrate improvement in deep time.
Significance of the two-headed hyphalosaurus fossil discovery
The preservation of this two-headed Hyphalosaurus fossil is a rare stroke of luck, contemplating that the fossil report captures solely a minute fraction of all organisms that after lived. Developmental anomalies like axial bifurcation are rare to start with, and their fossilization is much more unlikely. What makes this discovery much more outstanding is the specimen’s almost pristine situation.The fossil stays partially embedded in sediment, and the encompassing stone slab is unbroken, lending robust assist to its authenticity, a vital level given the area’s historical past of fossil forgeries.According to the unique 2007 examine revealed in Biology Letters, this fossil represents the oldest confirmed case of axial bifurcation in any vertebrate. Its discovery not solely sheds gentle on rare congenital situations in historical reptiles but in addition expands our understanding of how such anomalies have occurred all through evolutionary historical past. It serves as a rare and beneficial reference level for learning embryonic improvement, mutation, and survivability in extinct species.The Hyphalosaurus fossil discovery underscores the rarity of axial bifurcation and the worth of well-preserved specimens in learning prehistoric life. While fashionable examples of two-headed reptiles exist, this dinosaur-age fossil gives a novel glimpse into evolutionary improvement and the challenges of survival for such anomalies.By analyzing fossils like this, scientists acquire deeper perception into the variety and complexity of life hundreds of thousands of years in the past, emphasizing the persevering with significance of paleontology in uncovering nature’s historical mysteries.Also learn| 26-million-year-old whale cranium fossil discovered, sheds gentle on historical marine life